EnviroTech Services, Inc. takes water conservation seriously. We have covered water shortages impacting the Colorado River and highlighted water management efforts by the state of Nevada. Although this is an alarming issue, it is important to remain hopeful and review how states around the country are addressing water shortages.
In the past twenty years, California has been devastated by water shortages. A majority of the water supply in California comes from the Colorado River, which has seen rapid reduction. In response to the water crisis, the state of California is utilizing desalination plants. Desalination plants convert salt water into fresh water by using a chemical or physical process to reduce salt concentrations.
The development of desalination plants has been a slow process, but has gained momentum due to the need to address water shortages. The first desalination plants where built in the 1960s; this has grown to approximately 20,000 plants globally. Over 300 million people are currently relying on desalination plants as their water source.
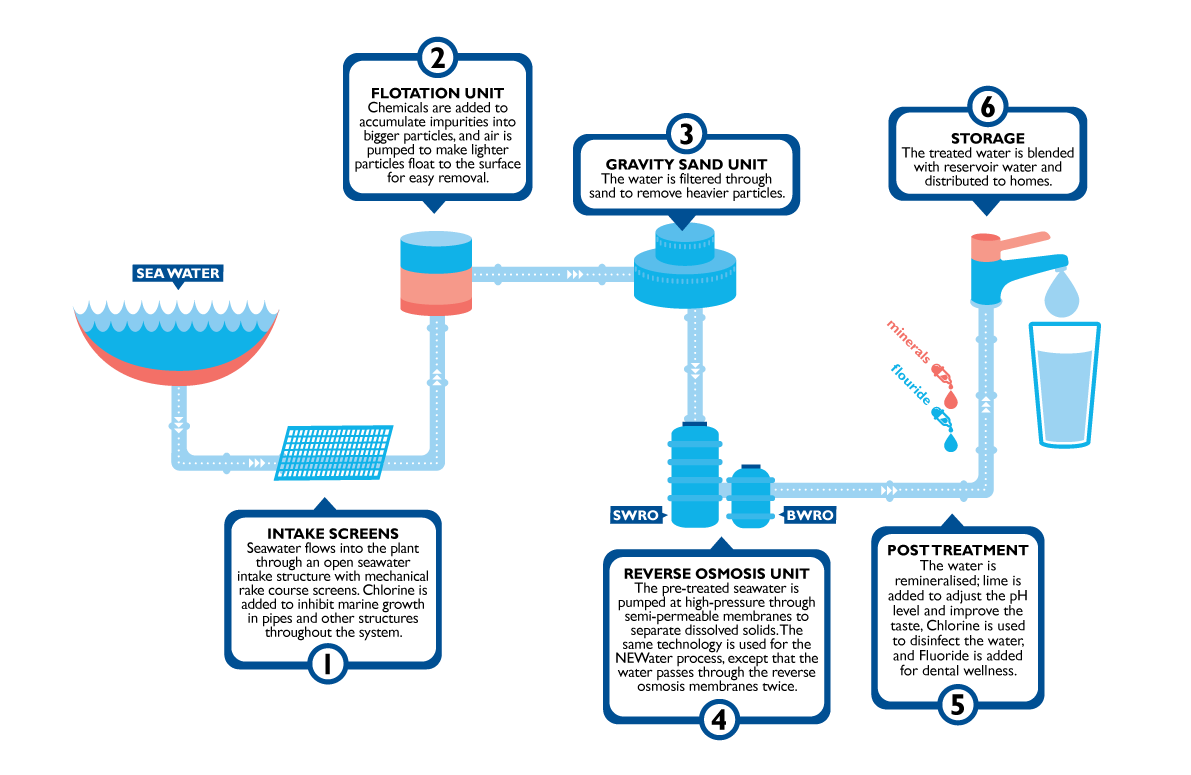
Image by Singapore's National Water Agency
The Claude “Bud” Lewis Carlsbad Desalination Plant on the Pacific Coast is the largest operation turning salt water into fresh water. Over 100 million gallons of seawater are pumped into the plant’s semi-permeable membranes, which produces around 50 million gallons of drinkable water. The Carlsbad plant started operation in 2015, and provides 10% of fresh water to the 3.1 million people in the San Diego region. The Carlsbad plant won an international award for technological and environmental achievement in 2016.
 Carlsbad Desalination Plant
Carlsbad Desalination Plant
The desalination process works, but at what cost? It costs approximately twice as much as the other main water source, the Colorado River. This technology is so expensive because it is still very new; it is expected to decline as technology evolves.
Although the desalination process addresses one environmental issue, it results in others. The amount of energy required for the desalination process has substantially increased the burning of fossil fuels. Another concern is the damage to ocean and marine ecosystems. The threat desalination plants pose to marine life is not entirely known, which makes potential consequences risky. California is attempting to address the environmental threat posed by desalination plants with restrictive policies, such as the Desalination Amendment passed in 2016.
There are many improvements to be made, but the state of California remains hopeful about how desalination plants can address water shortages. Desalination plants have the potential to replace reliance on water sources hundreds of miles away.
Works Cited
Creative, RetroMotion. “Desalination and the California Water Shortage.” ISI Water, 8 Nov. 2016, isi-water.com/desalination-california-water-shortage/.
Robbins, Jim. “Desalination Is Booming as Cities Run out of Water.” Wired, Conde Nast, www.wired.com/story/desalination-is-booming-as-cities-run-out-of-water/.